QUESTIONS ABOUT MICROWORLD
Pr M. Kanarev,
E-mail: kanphil@mail.ru, from ‘525_Kanarev_Questions.doc’
Brief answers to all 525 questions are available in the Internet in Russian, site: http://Kanarev.innoplaza.net Article 104.
Detailed answers to all 525 questions are published in the study guide: Kanarev Course of lectures in physchemistry of the microworld, 2nd edition. Krasnodar 2007. 540 pages (in Russia).
Additional information concerning all given questions is published in the monograph of Kanarev Ph.M. The Foundations of Physchemistry of the Microworld. 8th edition, Krasnodar 2007, 750 pages (in Russian).
– 1. What does the notion microworld mean?
– 2. What particles are considered to be the fundamental ones?
– 3. Since when has the man begun studying microworld?
– 4. In what form did Euclid represent the results of his scientific analysis of light behaviour?
– 5. What theories of the 20th century are devoted to the analysis of microworld inhabitant behaviour?
– 6. Why have Einstein’s relativity theories been criticized since the day of their emerging and why has their reliability not been established as yet?
– 7. Why has science failed to form a criterion, which would not depend on a subjective opinion of any scientist, to estimate a connection of any theory with reality?
– 8. Which scientist was the first to make a fundamental colligation in exact sciences, on which they are based as yet?
– 9. Which scientist made the second fundamental conclusion in exact sciences, which resulted in the technical revolution?
– 10. Why did the development of physical and chemical theories, which can describe diversity of behaviour of microworld being opened by the experimenters, slowed down considerably at the end of the 20th century?
– 11. Is there any necessity in the third fundamental conclusions in exact sciences and what should the essence of this conclusion be?
– 12. Why has science no consistent definitions of notions of Axiom and Postulate?
– 13. What is the difference between an axiomatic assertion and a postulated assertion?
– 14. Why did the scientists fail to establish the main scientific notions and rank them according to a significance level for the scientific investigations?
– 15. What axioms result from the main scientific notions and what is their role in the scientific investigations?
– 16. Why is there no international agreement between the scientists concerning a necessity to use the axioms and the postulates in order to estimate a connection of the existing physical and chemical theories and the new ones with the reality?
– 17. Does an axiom value depend on its recognition by the scientific society?
– 18. What criteria is a postulate value determined by?
– 19. What role does the space-matter-time unity axiom play in exact sciences development?
– 20. Do Lorentz transforms conflict with the space-matter-time unity axiom?
– 21. Can Lorentz transforms be considered as a theoretical virus?
– 22. What is the essence of a global contradiction between the space-time unity axiom, on which physics of the 20th century has been based, and the space-matter-time unity axiom, on which physics of the 21st century will be based?
– 23. Why is the fruitless physical theory elaboration process not stopped yet?
– 24. Does the unity axiom restrict an application range of Riemann geometry?
– 25. Is it possible to use a mathematical sign of photon velocity in the mathematical models of Riemann geometry?
– 26. Does the unity axiom restrict an application range of Louis de Broglie equations, Schrodinger equations and Maxwell equations?
– 27. Does the unity axiom restrict an application range of the partial derivatives?
– 28. Can Lobachevskian geometry and Minkowskian geometry be used in exact sciences?
– 29. Does the unity axiom admit a use of complex numbers in order to analyse the phenomena and the processes?
– 30. What dimensionality has Planck constant h=mA2v –> kg . m2 . s-1?
– 31. Is Planck constant h. =mA2v a vector value?
– 32. What physical meaning has dimensionality of Planck constant h = mA2v –> kg . m2 . s-1 ?
– 33. What law governs Planck constant permanency?
– 34. What postulate should be enunciated in order to remove a contradiction between a photon rotation process, which results from dimensionality of Planck constant, and its wavelength l, which reflects its wave features?
– 35. What physical meaning has dimensionality of Planck constant, which contains radius r of rotation instead of the wavelengthA (h=mr2v–> kg×m2×s-1)?
– 36. What photon structure results from the condition when the above-mentioned contradiction is eliminated when the wavelength A of the photon is equal to radius r of its rotation?
– 37. What brings the visual environment information into our eyes?
– 38. Can an ability of our eyes to perceive the smallest details of the visual environment serve as an indirect proof of localization (restriction) of the carriers of these details in space?
– 39. Who called an elementary carrier of energy a photon?
– 40. What is an electromagnetic structure of the photon?
– 41. What are the sizes of an area of space where the photon is localized?
– 42. How are the main parameters of the photon called?
– 43. Velocity C of the photon, its wavelength A and frequency v are connected by dependence C=Av. Does it appear from this that the photon is a wave, not a particle?
– 44. In what way are mass of the photon m, its wavelength A, rotation radius r, linear frequency v, Planck constant h, angular velocity w, amplitude of oscillations a, oscillation period T, velocity C and energy E are connected with each other?
– 45. In what range are mass, wavelength and energy of the photons changed?
– 46. What law governs localization of the photons in space?
– 47. What is a photon localization constant equal to?
– 48. Why is photon velocity of all ranges alike and equal to velocity of light ?
– 49. What law governs velocity permanency of motion of the photons of all frequencies?
– 50. Why is energy of the photons of all frequencies determined in accordance with two formulas E=mC2 and E=h×v?
– 51. At which quantity of electromagnetic fields of the photon is energy intensity of the processes of its rotation and of straight line motions a minimal one?
– 52. Can the electromagnetic fields of the photon play the role of its mass?
– 53. What does a minimal wavelength of the photon amount to?
– 54. What does maximal frequency of the photon amount to?
– 55. What does maximal mass of the photon amount to?
– 56. What does maximal energy of the photon amount to?
– 57. What does maximal wavelength of the photon amount to?
– 58. What does minimal frequency of the photon amount to?
– 59. What does minimal mass of the photon amount to?
– 60. What does minimal energy of the photon amount to?
– 61. What forces localize the photon in space?
– 62. How are the structure and the geometrical dimensions of the photon modified with a change of the wavelength, frequency, mass and energy of electromagnetic radiation?
– 63. Are there any reasons to use the notion of a photon emission scale instead of an erroneous name an electromagnetic emission scale?
– 64. In what range of the photon emissions do the solitary photons appear?
– 65. Where is a boundary on the photon (electromagnetic) emission scale, which divides this scale into a range of a nascence and an existence of the solitary photons and their aggregates and a range of an absence of the nascence of the solitary photons and a presence of their aggregates in the form of the waves only?
– 66. Why do the photons changing its wavelength and frequency in such a wide range have the same rate of propagation, which amounts to velocity of light?
– 67. Why is frequency decreased with an increase of the wavelength of electromagnetic emission?
– 68. Why is penetrating power of the photons increased with a decrease of their wavelength and an increase of mass and frequency?
– 69. Why do the photons fail to exist at rest?
– 70. Why do the photons possess the properties of a wave and a particle simultaneously?
– 71. Has the photon the center of mass and along what path does it move?
– 72. Along what path do the centers of mass of the electromagnetic fields of the photon move?
– 73. When were the wavy cycloid equations obtained and where were they published for the first time?
– 74. Why was it the first article being published by the author, without co-authors?
– 75. Why do the photons move rectilinearly?
– 76. Why are the photons polarized?
– 77. Why do the photons possess no charge?
– 78. Why are the photons indivisible?
– 79. In what way is the amplitude of oscillations of the center of mass of the photon connected with its wavelength?
– 80. In what way is Heisenberg inequation connected with the structure of the photon and its geometrical parameters?
– 81. Heisenberg inequation restricts accuracy of geometrical and kinematic experimental information. Does this inequation exert influence on accuracy of theoretical information?
– 82. Are velocities of the photon and a transmitter, which produces it, added?
– 83. Are velocities of the photon and a receiver added?
– 84. Pertaining to what is velocity of the photon constant?
– 85. Why did A. Einstein in his postulate: Any ray of light moves in the stationary system of co-ordinates with the determined velocity c, whether the ray be emitted by a stationary or by a moving body fail to mention pertaining to what velocity of light is constant?
– 86. Will a significance of this postulate be increased for exact sciences if the 2nd postulate by Einstein is enunciated in the following way: Velocity of the photons being emitted by a stationary or by a moving transmitter is constant pertaining to space and does not depend on a travel direction of the transmitter and its velocity?
– 87. Does the adjusted enunciation of Einsteins postulate regenerate Newtons ballistic hypothesis and what restricts take place in that case?
– 88. Has the photon some hidden parameters?
– 89. Is it possible to derive analytically all earlier postulated mathematical models, which describe the photon behavior, with the help of the hidden parameters?
– 90. What equations describe a motion of the center of mass of the photon within the framework of the unity axiom?
– 91. How is velocity of the center of mass of the photon changed within the range of its wavelength?
– 92. Is it possible to derive Louis de Broglie equation and Schrodinger equation from the equations of the short-cut cycloidal curve, which describes a motion of the center of mass of the photon?
– 93. Can a photon, which has appeared, decrease its wavelength?
– 94. Can a photon, which has appeared, increase its wavelength?
– 95. Why can the thermal photon exist in a free state or as a part of the electrons when they are in the atoms?
– 96. Why can the gamma photons exist in a free state or as a part of the protons arranged in the atomic nuclear?
– 97. Can the gamma photons be the thermal energy carriers?
– 98. Within which limits is the wavelength of the photons, which form thermal energy, changed?
– 99. Spin characterizes a particle rotation. Has the photon the spin?
– 100. What value plays a role of spin with the photon?
– 101. How is spin of the photon directed in relation to a path of its motion?
– 102. Do the spins of the photons interact when their motion paths intersect?
– 103. Does the photon spin reciprocity change their motion direction?
– 104. Why do the light monochromatic rays drift together when the circular polarization is similar and why are they pushed away when the circular polarization is different?
– 105. At what distance from each other do the light photons with the similar circular polarization begin to drift together?
– 106. Is the distance, at which the paths of the photons with similar circular polarization begin to drift together, in large excess over their radii?
– 107. Does the photon spin reciprocity exert an influence on a diffraction pattern formation when their motion paths intersect?
– 108. Has a reflected photon a transversal constituent of the pulse?
– 109. Why is an incident angle of the photon equal to a reflection angle despite of an orientation of the rotation plane (photon polarization)/
– 110. Why are the photons polarized by the reflection plane in two mutually perpendicular directions?
– 111. Why is larger part of the reflected photons polarized in the incidence plane and the reflection plane?
– 112. Why is smaller part of the reflected photons polarized in the plane, which is perpendicular to the incidence plane and the reflection plane?
– 113. Why is light reflectance equal to zero when Brewster angle is available and the planes of incidence, polarization and reflection coincide?
– 114. Why does the photon beam form the diffraction patterns and the interference ones?
– 115. The diffraction pattern behind the wire passes off if the wire contour is closed from one side. Why?
– 116. Why are the internal diffraction fringes formed by the photons, which interact with the opposite edges of the obstacles forming the diffraction patterns?
– 117. Why are the external diffraction fringes formed by the photons moving from the point light source and being reflected from the edges of the obstacles forming the diffraction patterns?
– 118. Why is an abnormal interference pattern formed between two slots or holes, the distance between which is comparable with the wavelength of the photon?
– 119. What errors did Fresnel make when he deduced the formula for a calculation of the diffraction bands behind the wire?
– 120. Is there a derivation of Fresnel formula for a calculation of the diffraction bands behind the wire, which differs from the derivation being suggested by Fresnel?
– 121. Does the new derivation of Fresnel formula exert an influence on an interpretation of the wave properties of light?
– 122. Does variable speed of motion of the centers of mass of the photons exert an influence on a formation of Newton iridescent rings?
– 123. Why do all elementary particles interacting with the obstacles form the diffraction patterns alike the wave patterns?
– 124. Has the photon velocity of light at once after the reflection or nascence or does it move with acceleration at first?
– 125. Does the photon lose energy in the transient phenomenon?
– 126. What experiment proves a loss of energy by the reflected photon clearly and with the high accuracy?
– 127. It is possible to assume that an infrared bias of the spectral lines of the atoms in the astrophysical observations is a proof of the loss of energy by the photons, which form these spectral lines?
– 128. How does the photon play the role of the elementary carrier of energy?
– 129. What type of energy forms an aggregate of the photons?
– 130. Does the law of an absolute blackbody serve as a proof that the photons generate thermal energy?
– 131. Does the mathematical model of the law of absolute blackbody emission serve as a proof that this law is the law of classical physics, not on the contrary, as it was supposed up to now?
– 132. What components of the law of absolute blackbody emission reflect an implementation of several laws of classical physics in this law?
– 133. In what ways is the mathematical symbol interpreted in the law of absolute blackbody emission?
– 134. In what ways is an aggregate of the mathematical symbols hv interpreted in the law of absolute blackbody emission?
– 135. In what ways is an aggregate of the mathematical symbols 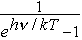 interpreted in the law of absolute blackbody emission?
interpreted in the law of absolute blackbody emission?
– 136. In what ways is an experimental coefficient  interpreted in the law of absolute blackbody emission?
interpreted in the law of absolute blackbody emission?
– 137. In what ways is the whole aggregate of the mathematical symbols interpreted in the law of absolute blackbody emission?
– 138. What mistakes were made in an interpretation of the mathematical models of the law of absolute blackbody emission and what negative influence did they exert in development of physics?
– 139. What law determines maximum of absolute blackbody emission density?
– 140. Is it possible to use Wien law in a determination of the wavelength of the maximal aggregate of the photons, which form a temperature in a definite point of space?
– 141. What aggregate of the photons determines a temperature in any point of space?
– 143. What role Wien law and its mathematical model play in the determination of the temperature in any point of space?
– 144. What photons form thermal energy?
– 145. Where is a boundary on a scale of the photon (electromagnetic) emissions of an existence of the thermal photons?
– 146. Does the process of a continuous temperature change in the environment serve a proof that it is a consequence of a change of the wavelength of the maximal aggregate of the photons in this area of space?
– 147. By what value is energy of each photon changed, which aggregate determines the temperature in the given point of space when this temperature is changed by one degree?
– 148. By what value is the wavelength of each photon changed in their maximal aggregate forming the temperature in the given point of space when this temperature is changed by one degree?
– 149. By which minimal value of the degree can the temperature in the given point of space be changed?
– 150. Are there any instruments, which can register the minimal value of the change of the temperature in the given point of space?
– 151. Is there a law of temperature localization in any two points of space and how it is enunciated?
– 152. Is there a temperature localization constant in any two points of space and what does it equal to?
– 153. How can the temperature of any space body determined with the help of the law of temperature localization?
– 154. Why is the nonradiating element of the measuring device (the bolometer) cooled to a limit low temperature in order to determine the background radiation of the universe?
– 155. To what temperature was the bolometer cooled in order to study relic radiation by the Nobel laureates of the year of 2006?
– 156. Is the minimal temperature of the bolometer a limit, which determines the maximal wavelength of relic radiation?
– 157. Why did the authors of the experiment, in which relic radiation was determined, represent their experimental dependence as a continuous one and fail to show an area, in which they failed to determine intensity of radiation as there was no bolometer with lower temperature?
– 158. To what temperature should the bolometer be cooled in order to register the largest wavelength of relic radiation?
– 159. Is a maximal wavelength of relic radiation equal to a maximal possible wavelength of the photon?
– 160. Is an absence of the photons with the wavelength exceeding the maximal wavelength of relic radiation in the nature a proof of the existence the limit low temperature?
– 161. Why does the absolutely low temperature exist?
– 162. What is the wavelength of maximum of relic radiation equal to and is it possible to calculate it theoretically?
– 163. What is the maximal wavelength of relic radiation registered experimentally by the Nobel laureates of the year of 2006 equal to and is it possible to calculate it theoretically?
– 164. Why does relic radiation possess the highest intensity in a millimeter range?
– 165. What source forms relic radiation?
– 166. What process forms a maximum of relic radiation?
– 167. Why is relic radiation formed at the temperature, which is close to absolute zero?
– 168. Is relic radiation connected with the Big Bang?
– 169. What is the nature of the whole range of relic radiation?
– 170. How many maxima has a zone of relic radiation?
– 171. What processes are formed by two other maxima of relic radiation with smaller intensity and smaller wavelength (Fig. 5)?
– 172. What is the reason of anisotropy of relic radiation and what global corollary results from it?
– 173. Is the whole experimental dependence of relic radiation calculated satisfactorily with the help of Planck formula describing an absolute blackbody radiation?
– 174. Why are the differences between the experimental results and the theoretical ones increased with a decrease of the wavelength of relic radiation?
– 175. What is the maximal temperature in the universe equal to and is it possible to determine it theoretically and experimentally?
– 176. Why do the photons with the wavelength, which exceeds the maximal wavelength of relic radiation, fail to exist in the nature?
– 177. How is radiation with the wavelength, which exceeds the maximal wavelength of relic radiation, formed?
– 178. How many constants govern behaviour of the single photons?
– 179. How many constants govern behaviour of an aggregate of the photons?
– 180. A constant of photon localization governs a process of their localization in the interval of the gamma range to the maximal wavelength of relic radiation. All parameters of the photon in this range are changed almost by 15 orders of magnitude proving the corpuscular properties of the photons of all frequencies. Has the electron a constant of localization being a particle?
– 181. What is a constant of electron localization equal to?
– 182. Is the constant of electron localization equal to the constant of photon localization?
– 183. What is an electron radius resulting from the constant of its localization equal to?
– 184. In what digit after point does a value of the electron radius determined from its localization constant coincide with an experimental value of the Compton wavelength of the electron?
– 185. Is a coincidence of the theoretical value of the electron radius with an experimental value of the Compton wavelength in the sixth digit after point a sufficient reason for recognition of equality between the electron radius and its wavelength?
– 186. Are there the mathematical models for a theoretical calculation of the experimental radius of the electron accurate to the 6th digit after point?
– 187. If the theoretical value of the radius of the ring model of the electron coincides with an experimental value of the Compton wavelength of the electron in the 6th digit after point, can it be considered in the first approximation that the electron has a form of the ring?
– 188. What characteristics of the electron are introduced into the mathematical models in order to calculate its radius?
– 189. What electron phenomenon in the electron structure forms its magnetic moment and kinetic energy?
– 190. Is there any reason to suppose that the electron has the second rotation?
– 191. What structure should the electron have when two rotations are available?
– 192. Will the energy of two rotations be equal to photon energy Ee =m eC2 of the electron if it is postulated that the electron has the form of a hollow torus, which is rotated in relation to the axis of symmetry and in relation to a ring axis?
– 193. Why does angular velocity wp of vortex rotation of the electron exceed angular velocity we of its rotation in relation to axis of symmetry 6fold?
– 194. What electromagnetic phenomenon in the electron structure forms its electrical charge and potential energy?
– 195. Why is a theoretical value of kinetic energy of the electron equal to a theoretical value of its potential energy?
– 196. Why is a sum of the theoretical values of kinetic energy Ekand potential energy E0 of the electron equal to its photon energy Ee =m eC2?
– 197. Why is photon energy equal to a product of Planck constant by linear frequency E=hv and electron energy to a product of Planck constant by angular velocity of its rotation E=hwe?
– 198. Why can the electron exist in quiescence as distinct from the photons?
– 199. What laws govern rigidity of electromagnetic structure of the electron?
– 200. Why are mass, charge and radius of the electron the constant values of a free electron?
– 201. Can the electron exist in a free state without a restoration of its mass when a photon has been emitted?
– 202. Where does the electron take mass for a restoration of stability of its free state mass when a photon has been emitted?
– 203. Can it be supposed that the electron restores its mass absorbing a substance of its environment being called ether?
– 204. Are there any quantitative characteristics of ether?
– 205. Why is spin of the electron equal to Planck constant, not to its half as it has been considered so far?
– 206. How is a vector of magnetic moment of the electron directed in relation to a direction of its spin?
– 207. Why do the vectors of angular momentum and magnetic moment of the electron coincide in their direction rather than directed oppositely as it has been supposed so far?
– 208. Can the electron be turned into a photon? Is there an experimental proof to it?
– 209. What is energy of the photons being formed from the electron equal to?
– 210. To what range of a scale of the photon emission does the photon issued from the electron belong?
– 211. What is angular velocity of rotation equal to if energy of the electron likewise energy of the photon is determined via Planck constant and the electron should rotate in relation to the axis of symmetry?
– 212. Why is angular velocity of rotation of the free electron a constant value?
– 213. In what cases is angular velocity of rotation of the electron changed?
– 214. What processes take place in the electromagnetic structure of the electron if its rotation in relation to the axis of symmetry is retarded?
– 215. Will a sign of an electron charge be changed if kinetic rotation of the electron in relation to the axis of symmetry is changed by an opposite one?
– 216. Why is the charge sign changed when a direction of kinetic rotation of the electron is changed, and it turns into a positron?
– 217. Why is the positron an unstable electromagnetic formation?
– 218. In what cases can mass of the electron be changed?
– 219. Can mass of the electron, which moves in the electrical field, be increased and according to what law?
– 220. Can a mathematical model of a relativistic law of a change of mass of the electron moving in the electrical field be derived from the laws of classical physics?
– 221. What is the essence of a physical process of an increase of mass of the electron moving in the electrical field?
– 222. As the electron behaviour as well as the photon behaviour is governed by the law of its localization in space, its radius should be decreased with an increase of mass of the electron. In what measurement device is this effect used?
– 223. What is magnetic field density equal to near the center of symmetry of the electron?
– 224. According to what law is density of the magnetic field of the electron decreased along the axis of its rotation?
– 225. If the electron has the magnetic filed, which is similar to the magnetic field of the bar magnet, the unlike magnetic poles of the electrons should bring them together, and the like electric charges should restrict this rapprochement. In this connection, a question arises: can the electron clusters be formed and are there the experimental evidences to it?
– 226. In what simplest process is this phenomenon observed?
– 227. Light being formed by an electric spark is the photons being emitted by the electrons when they and the ions form a cluster. How will a colour of the spark be changed if voltage is increased and why?
– 228. What process generates a crackling when an electric spark is formed?
– 229. Are the clusters of the electrons and the ions formed in the nature?
– 230. What natural phenomenon is a result of the formation of clusters of the electrons and the ions?
– 231. Are electric spark crackling and thunder-blasts of lightning formed by one and the same process or by different ones?
– 232. What processes are formed by linear lightning in the clouds?
– 233. Are the aggregates of electrical charges formed uniformly in the clouds or no? What phenomenon proves this nonuniformity?
– 234. What forces prevail when lightning is formed: electrostatic or magnetic forces? By what features of lightning can it be judged?
– 235. On account of what do the electrons of the clusters, which have emitted the photons (and there is a lot of them), restore their masses?
– 236. What elementary particles can be formed in the electron clusters of lightning?
– 237. Can an explosion of the electron population and a formation of a new star take place if an aggregate of the electrons is formed by many orders of magnitude greater in any area of space environment than during a thunderstorm on the Earth?
– 238. Is there any reason to suppose that the protons and the neutrons, the main components of the atomic nuclei, can be formed during an explosion of the large aggregate of the electron clusters?
– 239. Are there any hypothesis explaining the essence of a process of emission of the photons by the electrons?
– 240. Are there any hypothesis explaining a process of absorption of the photons by the electrons?
– 241. Is the constant of localization of the proton equal to the constant of localization of the electron and the photon?
– 242. To what extent is the proton rotation radius less than the electron rotation radius?
– 243. What structure has the proton in the first approximation?
– 244. To what extent is proton magnetic field density larger than electron magnetic field density near their geometrical centres?
– 245. It appears from Bohr postulate that the length of the electron orbit is equal to the length of its wave when the main quantum number n=1. Can this contradiction be put up with?
– 246. According to what law resulting from the orbital motion of the electron are energies of the absorbed and emitted photons changed during a transit of the electrons between the orbits?
– 247. How does the electron interact with the proton of the atomic nucleus: linearly or orbitally?
– 248. Can the unlike electric charges of the electron and the proton bring them together when they form the hydrogen atom? Can the like magnetic poles restrict this rapprochement?
– 249. Are there theoretical and experimental evidences of an absence of the orbital motion of the electron in the atom?
– 250. Are energies of the single photons and the single electrons the vector values?
– 251. If the electrons absorb and emit the photons, addition and deduction of their energies as vector values should be carried out in accordance with the rules of vector algebra. What experimental results prove this fact?
– 252. Can Bohr mathematical model for a hydrogen atom spectrum calculation, which results from the orbital motion of the electron, be derived from the process of a linear interaction of the electron with the proton of a nucleus of any atom?
– 253. How are the vectors of spin and magnetic moment of the proton directed?
– 254. How many energy levels have the electron of the hydrogen atom and the electron of other atoms?
– 255. According to what law is binding energy Eb of the electron with the proton of the nucleus of any atom changed?
– 256. According to what law are energies of the photons EPh, which are absorbed by the electrons during their consequent jump from the lower energy levels to the upper ones?
– 257. According to what law are energies of the photons EPh, which are absorbed by the electrons during their consequent jump from the upper energy levels to lower ones?
– 258. Is there any mathematical model for a calculation of the spectrum of any electron and any atom? Is it possible to consider this model a law of the formation of the spectra of the atoms and the ions?
– 259. Does an absence of the orbital motion of the electron in the atom result from the law of the formation of the spectra of the atoms and the ions?
– 260. What structure has the hydrogen atom?
– 261. Why are the ionization energies of the hydrogen-like atoms proportional to a square of the protons in the nucleus?
– 262. Why is the ionization energy of the first electron of the helium atom twice as much the ionization energy of the hydrogen atom and the ionization energy of the second electron of the helium proportional to a product of ionization energy of the hydrogen atom by a square of the main quantum number?
– 263. Are there fictitious binding energies of the electrons with the protons of the atomic nuclei?
– 264. Why is ionization energy of one electron of the lithium atom less than ionization energy of the electron of the hydrogen atom?
– 265. Why are binding energies of all four electrons of the beryllium atom similar on the like energy levels under the condition when they all are in the atom?
– 267. Does equality of binding energies of all electrons of the beryllium atom on the like energy levels result from the experiments?
– 268. Is the electron mass changed when it absorbs and emits the photons?
– 269. Is the electron radius changed when it absorbs and emits the photons?
– 270. What is the limit energy of the photon, which is emitted by the electron during the formation of the atoms and the ions, equal?
– 271. As the dimensions of the photons being emitted by the electron can be by many orders of magnitude greater than the dimensions of the electrons, isnt it the main factor, which determined shooting range?
– 272. The electron radius can be equal to the photon radius. In what range of the photon radiation scale is this photon and what is the length of its wave equal to?
– 273. In what way is the Compton wavelength of the electron connected with its radius?
– 274. What law governs constancy of the Compton wavelength of the electron?
– 275. Why is intensity of the shifted component decreased in the Compton effect with an increase of the chemical element number?
– 276. Why is the Compton effect registered only in case when the X-ray photons are used?
– 277. Is the law of conservation of energy observed in the Compton effect?
– 278. Is there a connection between the mathematical models of the formation of the spectra of the atoms and the ions and Einstein mathematical model, which describes a photoeffect phenomenon?
– 279. What actual physical sense has a work function in the mathematical models of the photoeffect being suggested by A. Einstein?
– 280. Does the mathematical model of the law of the formation of the spectra of the atoms and the ions make it possible to determine a source of the photoelectrons in the photoeffect phenomenon? Do the atoms or the molecules emit the photoelectrons in the photoeffect phenomenon?
– 281. Does an absence of the orbital motion of the electrons in the atoms simplify a description of the processes of fusion and dissociation of the molecules and the clusters?
– 282. Does an absence of the orbital motion of the electrons in the atoms simplify the chemistry textbooks and will it increase attractiveness of chemistry as science for the youth?
– 283. Does the photon emitted by the electron move with acceleration or has it velocity of light at once?
– 284. How does electron absorb and emit the photons during the energy jumps in the atoms, the ions and the molecules?
– 285. Why does an explosion take place when hydrogen is combined with oxygen?
– 286. In what way do the electrons combine the atoms into the molecules if they fly in orbit round the atomic nuclei?
– 287. What forces combine the atoms into the molecules during the orbital motion of the electrons?
– 288. How are the hindrances of the mutual influence of the electrons flying in the orbit on the processes of the formation of the molecules of various complexities eliminated?
– 289. How are molecule clusters formed during the orbital motion of the electrons in the atoms?
– 290. What forces combine the molecules into the clusters during the orbital motion of the electrons in the atoms?
– 291. Why is the erroneous orbital theory of motion of the electrons in the atoms, which has a lot of contradiction, is recognized implicitly by modern physicists and chemists?
– 292. Are there experimental evidences that the electron has the so-called classic radius of the electron?
– 293. What strictest experiment proves the corpuscular properties of the electrons?
– 294. Why does the electron being a particle form the diffraction patterns and the interference patterns, which are similar to the patterns being formed by the photons?
– 295. In what way does the electron of the hydrogen atoms, which has no orbital motion in the atom, interact with the protons?
– 296. What forces bring the electron with the proton together and what forces limit this rapprochement?
– 297. Is a size of the hydrogen atom in large excess over a size of the proton and the electron?
– 298. What number of energy level of the electron of the hydrogen atom is the initial one at the time when a contact has been established between the electron and the proton and from what experiment does it result?
– 299. What factor limits the upper energy level of the electron in the atom?
– 300. In what natural phenomenon is statistic of the photons, which are emitted by the hydrogen atom during its formation, reflected?
– 301. Why is a spectral line, which corresponds to ionization energy of the hydrogen atom, absent?
– 302. What do the hydrogen atoms exist in a free state only in case if the temperature exceeds 2700°C?
– 303. On what energy levels are the electrons of the hydrogen atoms when a hydrogen molecule is formed?
– 304. How do two hydrogen atoms form the hydrogen molecule? What forces bring these atoms together and what forces limit their rapprochement?
– 305. Why are the spin vectors of all electrons and all protons in the hydrogen molecules directed in one and the same direction?
– 306. Why do the orthohydrogen molecules and the parahydrogen ones exist?
– 307. Magnet moment of what particle divides the hydrogen molecules into the orthohydrogen molecules and the parahydrogen ones?
– 308. Why all hydrogen molecules acquire a structure of parahydrogen when the temperature is decreased?
– 309. How are the vectors of spins and magnet moments of the protons and the electrons in the atoms and the hydrogen molecules directed?
– 310. What elementary particles can be formed by the clusters?
– 311. Can the clusters form the molecules?
– 312. Do the electrons or the protons of the hydrogen atoms combine the water molecules into the clusters?
– 313. If the water molecules combine the protons of the hydrogen atoms into the clusters, by how many orders is a geometrical size of such contact smaller than two water molecules combined into a cluster if they are represented spherically?
– 314. If the contact size is less that a size of two molecules by 6 or 7 orders, isnt it the main reason of fluidity of the water molecules?
– 315. How many molecules can be in a water cluster?
– 316. How are the binding energies changed in the cluster of the water molecules?
– 317. Why water expends when it freezes?
– 318. Why have the snowflakes an openwork hexagonal form?
– 319. Why does an aggregate of the clusters of the water molecules acquire a hexagonal form when water is treated by melodic classical music fro a long time?
– 320. Why do the water clusters form the openwork hexagonal formations when they are treated by a still voice of a prayer?
– 321. Why does water, which has been treated by a voice of the prayer for a long time, acquires the medicamentary properties?
– 322. Why does water form the clusters of the chaotic forms when it has been treated by jive?
– 323. Can a prolonged influence of jive on a human organism form the clusters of the water molecules of the chaotic form, which cause various diseases inevitably, in the organism?
– 324. How are the musical melodies connected with a process of a change of the binding energies between the water clusters?
– 325. Will the mankind learn to use the process of the formation of the harmonic water clusters in the human organism for health strengthening?
– 326. Is the cluster formation process endothermal or exothermal?
– 327. How many electrons can a water molecule have?
– 328. In normal state, a water molecule has 10 electrons; eight of them belong to the oxygen atom and two electrons belong to the hydrogen atoms. Are there 10 electrons in the water molecule?
– 329. Can a water molecule have 9 electrons?
– 330. Can a water molecule have 8 electrons?
– 331. Can a water molecule have 11 electrons?
– 332. Can a water molecule have 12 electrons?
– 333. If all molecules of one litre of water have by one electron more or less as compared with the normal state, can this difference be registered by a weight method with the help of the measurement instruments?
– 334. Are the hydrogen atoms connected always only to the axial electrons of the oxygen atom?
– 335. Can the hydrogen atom be connected to a circular electron of the oxygen atom in the water molecule?
– 336. Why is the hydroxonium formation process an endothermic one?
– 337. What properties are imparted by hydroxonium to water?
– 338. Can the proton of the hydrogen atom in the water molecule be in a free phase state and form its acidic properties in this manner?
– 339. Why is the hydrogen dioxide formation process an endothermic one?
– 340. Do the electrons of the hydrogen atoms or the oxygen atoms absorb the photons before the formation of a hydrogen dioxide molecule?
– 341. Is it possible to attachOH– ions to all six ring electrons of the oxygen atom in a water molecule?
– 342. Why has pure water infinitely large electrical resistance?
– 343. Why is electrical resistance of water decreased if an alkaline ion or an acid ion is introduced into water?
– 344. Can water accumulate large electric potential?
– 345. Why is large electric potential accumulated in water when an alkaline solution of water goes through plasma oftentimes?
– 346. Why does plasma take place when a cathode area is decreased as compared with an anode area?
– 347. What temperature can plasma have when plasma electrolysis of water takes place? What does it depend on?
– 348. What phenomenon is generated by noise when plasma electrolysis of water takes place?
– 349. What does a gas exhaust depend on when plasma electrolysis of water takes place?
– 350. Is it possible to decrease quantity of hydrogen burning in plasma when plasma electrolysis of water takes place?
– 351. Why does a transmutation of the nuclei of chemical elements take place on a cathode surface when plasma electrolysis of water takes place? Can a plasma electrolytic process serve as a basis in the study of the transmutation of the nuclei of the atoms of chemical elements?
– 352. Why is additional thermal energy generated during the plasma electrolysis of water only in turbulent motion of the solution in the plasma zone?
– 353. Can electrical potential be accumulated in geological water in the high temperature zones? Can the underground lightings be formed?
– 354. What geological formations are formed by the underground lightings?
– 355. What form have the geological formations, which are formed under the influence of the underground lightings?
– 356. Why do the geological concretions consist of iron mainly?
– 357. Can such formation be met on the surface of the Earth or on the ocean bed?
– 358. Can excessive thermal energy be obtained if an influence is exerted on the ions and the clusters of water?
– 359. It is known that voltage for water heating can be supplied continuously and by pulses. What process is more effective when the influence is exerted on the ions, the clusters and the molecules of water?
– 360. Why is electric energy consumption for solution heating decreased and electric efficiency of the process increased when a preplasma operation mode is formed?
– 361. How does electric efficiency of the process of water solution heating depend on a value of a dielectric gap between the electrodes?
– 362. What is a value of direct energy efficiency in case of the pulse influence on the water solution: 100%, 1000%, 3000%, 5000%?
– 363. How does electric efficiency of the pulse processes of water solution heating depend on a pulse form?
– 364. How does electric efficiency of the pulse processes of water solution heating depend onpulse frequency?
– 365. How does electric efficiency of the pulse processes of water solution heating depend on pulse duration?
– 366. How does electric efficiency of the pulse processes of water solution heating depend on a duty ratio?
– 367. How does electric efficiency of the pulse processes of water solution heating depend on its density?
– 368. How is a process of additional thermal energy generation connected with a law of conservation of energy?
– 369. Can pulse energy efficiency of water solution heating be realized with the help of an electronic pulse generator?
– 370. What is the wording of a power formation law in an electric circuit, according to which the power is determined in its any section?
– 371. Why is the power formation law in the electric circuit discovered only at the beginning of the 21st century?
– 372. In what way was an existence of the power formation law in the electric circuit proved theoretically?
– 373. In what way was an existence of the power formation law in the electric circuit proved experimentally?
– 374. The electric circuit law wording is as follows: average power in any section of electrical network is equal to a product of an average value of voltage by an average value of current. What energy consequences result from this law?
– 375. How is an average value of voltage determined if voltage pulses have a triangular or rectangular form?
– 376. How is an average value of current determined if current pulses have a triangular or rectangular form?
– 377. By how many orders is power on the energy consumer terminals in the form of the synchronously changing pulses of voltage and current with 100 duty ratio smaller than power on the primary power source terminals with a constant process of voltage generation in accordance with the law of formation of electric circuit power?
– 378. Will power on the power supply source terminal be equal to power consumed by the pulses with 100 duty ratio in accordance with the law of formation of electric circuit power if the initial power supply source operates continuously?
– 379. By how many orders is power on the terminals of the above-mentioned power source being determined in accordance with the law of formation of electric circuit power larger than power on the energy consumer terminals being determined in accordance with the law of formation of electric circuit power as well and why?
– 380. What should be done that power on the electric energy pulse consumer terminals can be equal to power on the initial power source terminals?
– 381. If the initial power supply source produces voltage not continuously, but by the pulses corresponding to the voltage pulses on the consumer terminals, powers on the terminals of the power supply source and the consumer will be equal. Can it be apprehended?
– 382. What is the main parameter that restricts an increase of efficiency of the electromechanical generator of pulses?
– 383. Is it possible to create high performance electromechanical generators of pulses of voltage and current of various powers?
– 384. Synchronism of the formation and consumption of pulse electric energy is the main condition of power equality on the terminals of the primary power supply source and the consumer. What is a value of mechanical losses for an electromechanical generator drive in this power balance?
– 385. Can 30fold energy efficiency of the heat generation process exist if electric power on the consumer terminals is 30fold as little than thermal power generated by a pulse energy consumer when the electronic pulse generator is used according to the law of the electric circuit power formation?
– 386. What power supply source realizes energy efficiency of a pulse influence on the ions and clusters of water when it is heated?
– 387. What are the losses in the electromechanical generator of pulses?
– 388. Why is additional thermal energy formed in the ventilation systems and the hydraulic systems of water cavitation?
– 389. On what energy levels are the electrons of hydrogen atoms in water molecules?
– 390. Why is energy, which is spent on an electrodynamic or mechanic bond opening in the molecules of gases and liquids, less than energy of thermal rupture of these bonds?
– 391. By what value is binding energy between the hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atoms in the water molecules changed when it is heated by one degree?
– 392. How does mass of the molecules of gases and liquids depend on their temperature?
– 393. Why are the hot molecules of gases and liquids heavier that the cold ones?
– 394. In what technical devices is a difference of masses of the hot and cold molecules of liquids realized in order to obtain an effect?
– 395. In what technical devices is a difference of masses of the hot and cold molecules of air realized in order to obtain an effect?
– 396. In what natural phenomena is a difference of masses of the hot and cold molecules of air observed?
– 397. The existing theory of low voltage electrolysis of water forecasts a separation of the hydrogen atoms from the water molecules and further fusion of the hydrogen molecules. In this case, the hydrogen atoms pass a free state phase when plasma of atomic hydrogen is formed, but no plasma is formed in the actual low voltage processes of water electrolysis. Why?
– 398. Why does a theoretical calculation of hydrogen molecule fusion energy during the low voltage electrolysis of water show availability of additional thermal energy, but this energy is not available in the actual experiments in the manufacturing cycles of hydrogen production?
– 399. Is there a structure of the cells where a water electrolysis process takes place with average current of 0.02 A?
– 400. In what way does energy efficiency of the low current electrolyzer depend on a distance between the electrodes?
– 401. In what way does energy efficiency of gas production from water depend on solution density in case of pulse power supply of the electrolyzer?
– 402. In what way does energy efficiency of gas production from water depend on a geometric form of the electrodes in case of pulse power supply of the electrolyzer?
– 403. In what way does energy efficiency of gas production from water depend on a chemical composition of the solution in case of pulse power supply of the electrolyzer?
– 404. Why are the gases evolved in a low current electrolytic cell within many hours after the external power supply has been switched off?
– 405. How can this process be intensified and its duration be increased?
– 406. Why does a positive charge take place on the upper electrode and a negative charge on the lower one in an empty low current electrolytic cell?
– 407. Why does a potential appear at the electrodes of the low current electrolytic cell before it is filled in with the solution?
– 408. Why does a larger charge appear at the cell electrodes during filling-in of the low current electrolytic cell with electrolyte than at the electrodes of an empty cell?
– 409. Why is a potential at the electrodes of the low current cell not reduced to a zero?
– 410. Does a constant potential at the terminals of the operating electrolyzer reflect the electric energy expenses for an electrolysis process?
– 411. How can an influence of the constant potential at the electrolyzer terminals on water electrolysis process energetics be eliminated?
– 412. Can energy expenses for hydrogen production from water be reduced considerably?
– 413. Does productivity of the cell with the funnel shaped electrodes depend on their sizes?
– 414. Being charged, any electrolyzer acquires electric potential being equal to approximately two volts per cell. Further gradual reduction of this potential points at the fact that it can be charged not continuously, but by pulses. How can the electric energy expenses for a water electrolysis process be reduced in this case?
– 415. Is it possible to realize energy effect of pulse power supply of the electrolyzer in accordance with the law of power formation in the electric circuit if the primary electric energy source generates voltage continuously?
– 416. What primary electric energy source should be to make it possible to realize energy efficiency of the pulse power supply process of the electrolyzer in accordance with the law of electric circuit power formation?
– 417. What value will the law of electric circuit power formation have for future pulse energetics?
– 418. How is electromagnetic radiation in the form of the mutually perpendicular sinusoids resulting from Maxwell equations localized in space changing its main parameters (wavelength and frequency) in the range of 25 orders?
– 419. Why do Maxwell equations state a formation of some electromagnetic field, the structure of which has not been established yet, by a radio transmitter aerial contrary to the established fact that the photons are emitted by the electrons during their energy jumps in the atoms?
– 420. Why do Maxwell equations being obtained in the year of 1865 fail to discover an electromagnetic structure of electromagnetic emission and a structure of the photon in particular?
– 421. Is it possible to have trust in correctness of Hertz experiment interpretation concerning a emergence of induction in dielectric when it is influenced by emission?
– 422. Is there any reason to think that an introduction of dielectric in Hertz resonator zone forms an additional flow of the photons to the resonator, which are reflected from dielectric; it forms current in the resonator, which is called displacement current?
– 423. Is a direct experiment for a check of the induction phenomenon in dielectric possible?
– 424. Is there any reason to think that an electric component of Maxwell electromagnetic field induces current in a straight-line bar and a magnetic component induces current in a curved bar?
– 425. Is there any reason to think that current in the straight-line bar and the curved bar is induced by a photon flux, not by the electric and magnetic components of Maxwell electromagnetic wave?
– 426. Will operability of Maxwell equations be preserved if there is no induction phenomenon in dielectric?
– 427. Will operability of Maxwell equations be preserved if it is proved that no displacement current exists?
– 428. The photons are known to be emitted by the atomic electrons. What is emitted when the radio waves or a TV signal are formed?
– 429. Are the photon and the electromagnetic wave one and the same thing or they are different electromagnetic formations?
– 430. In what way does the photon function as an elementary carrier of information?
– 431. Why is propagation distance of a surface radio wave increased if its length is increased?
– 432. In what way does a radio wave, which length is measured in kilometres, transmit information to the receiver aerial, the dimensions of which can be several centimeters and even smaller?
– 433. In what way do the electrons transmit one and the same information simultaneously by wire and emit it into space?
– 434. With what velocity do the electrons move by wire in the process of Internet information transmission by them?
– 435. Can Internet information be transmitted by a process of electron motion by wire with velocity near to velocity of light?
– 436. Is it possible to transmit Internet information by wire with the help of the longitudinal waves being formed by pulse influences on the electrons along the wire?
– 437. What is displacement velocity of free electrons by the wire when the pulses influence them?
– 438. By how many orders is displacement velocity of free electrons by wire under the influence of an external pulse smaller than velocity of propagation of a longitudinal wave of a pulse interaction of the electrons?
– 439. How does the transmission process form Maxwell electromagnetic waves for information transmission into space if it is supposed that Internet information is transmitted by wire with the help of the longitudinal pulse waves of the interacting electrons?
– 440. Can the process transmit simultaneously one and the same information along the wire and perpendicular to it into space if it emits a photon, which is adequate to this influence, at the time of pulse influence on the electron in the wire?
– 441. Can we use a mathematical model of the Doppler effect calculation resulting from Lorentz transforms for a calculation of infrared spectrum displacement?
– 442. Is there a classical mathematical model of the Doppler effect calculation, which gives more precise results than the relativistic model?
– 443. Is the Doppler wave effect and the spectral line displacement effect one and the same phenomenon or are they different phenomena?
– 444. Do all stars of the universe form an infrared spectrum displacement?
– 445. Are there any stars in the universe, which form the ultraviolet spectrum displacements?
– 446. What spectrum displacement is larger: the infrared displacement or the ultraviolet one? To what extent and why?
– 447. Is there an unambiguous answer: is the universe extended or no?
– 448. What experiment should be conducted in order to get an unambiguous answer concerning the state of the universe? Is it extended or not?
– 449. Why is no wavelength of the photons, which are hindered by this hole, in Schwarzschild formula for a determination of a radius of a black hole?
– 450. By how many orders will the radius of the black hole being formed from a star with the parameters of the Sun be decreased if the photon wavelength is taken into account?
– 451. By how many orders will density of substance of the black hole with the parameters of the Sun if the wavelength of the photon hindered by such hole is taken into account?
– 452. What is the mistake of the determination of a value of a photon motion path deviation by the Sun gravitational field made by Eddington mission, which tried to prove appropriateness of Einsteins relativity theories?
– 453. How are the protons arranged in the nucleus if each of them interacts with its electron?
– 454. What particle screens the like electrical fields of the protons in the atomic nuclei?
– 455. What forces unite the protons and the neutrons?
– 456. How many protons can be added by one neutron?
– 457. How many protons are added by one neutron under actual conditions?
– 458. Why does the nucleus lose stability when the number of the neutrons in the nucleus of the hydrogen atom is increased?
– 459. Why are the forces connecting the protons and the neutrons of the nuclei not the central ones?
– 460. Why is a share of supernumerary neutrons increased when quantity of the protons and the neutrons in the atomic nuclei is increased?
– 461. Now, quantity of the nucleons is taken into consideration when specific binding energy between the nucleons of the nucleus is determined. Is it correct?
– 462. Will specific binding energy between the nucleons be decreased more intensely than during a registration of quantity of the nucleons in the nuclei if quantity of bonds between the nucleons in the nucleus is taken into consideration?
– 463. What is magnetic field strength near a geometrical centre of the proton and the neutron equal to?
– 464. According to what law is magnetic field strength of the protons and the neutron changed along the axes of their symmetry?
– 465. How many magnetic poles has magnetic field of the electron?
– 466. How many magnetic poles has magnetic field of the proton?
– 467. How many magnetic poles has magnetic field of the neutron?
– 468. What is magnetic field strength in the contact area of the proton with the neutron equal to?
– 469. What is the nature of the nuclear forces and why is their value decreased quickly decreased when the distance from the centre of the nucleus is increased?
– 470. Why have 100% of the beryllium nuclei 5 neutrons and four protons?
– 471. Why is carbon represented in the nature in two forms having different properties: brittle graphite and very strong diamond?
– 472. Why are the nuclei of the graphite atoms flat and the nuclei of diamond spatial?
– 473. Why are the numbers of the nuclei of helium, oxygen, calcium considered to be the magic numbers?
– 474. Why are oxygen, nitrogen and carbon the main components of combustible substances?
– 475. Why can the transmutation of the atomic nuclei take place at lower temperature than it has been considered so far?
– 476. What photons are emitted by the electrons during fusion of the atoms and the molecules?
– 477. What photons are emitted during fusion of the atoms and the molecules?
– 478. What photons form thermal energy in the nuclear reactors of the atomic power stations?
– 479. Can the emission being formed during fusion of the nuclei play the role of heat carrier heating?
– 480. What elementary particle of the nucleus emits gamma photons?
– 481. Why do the nuclei of the radioactive elements emit easily the nuclei of helium, which are called alpha particles and why are they dangerous for living bodies?
– 482. Why has the hellion a positive charge?
– 483. Have the protons of the atomic nuclei the energy levels similar to the energy levels of the electrons in the atoms?
– 484. How many energy levels have the protons of the nuclei?
– 486. What are the ionization energies of these nuclei equal to?
– 487. Are X-ray photons and thermal photons the thermal energy carriers?
– 488. Is it possible to transform X-ray photons and gamma photons into the thermal photons?
– 489. In what cases do the nuclear reactions emit thermal energy?
– 490. Does a neutrino exist in the nature?
– 491. Can a disbalance of masses be explained by a transformation of a part of mass into ether in some experiments?
– 492. What is the essence of the hypothesis substituting the neutrino and explaining all cases of disbalance of masses and energies, which have been registered in the microworld experimentally, more correctly?
– 493. What serves as building material of all elementary particles?
– 494. What particle was born the first? The photon? The electron? The proton? The neutron?
– 495. What is the nature of a ball lightning?
– 496. Can a complex electromagnetic structure be formed, which can remain at rest or move with speed being considerably less than speed of light, if the polarization planes of the photons, which have similar wavelength at the time they are born, are perpendicular?
– 497. Are the unidentified flying objects the complex electromagnetic formations with the structure, which is unknown to us?
– 498. Can stable annual plasma be generated in a thermonuclear reactor if we take into account that the photons, which form it, have straight line motion and do not interact with the magnetic field?
– 499. Is it possible to make an electron of the structure, which has already been known to us, move stably along a tokomak ring?
– 500. What mistake was made by Michelson and Morley when they interpreted their famous experiment?
– 501. Why do Michelson-Morley experiment results disagree with the results of Sogniac experiment?
– 502. Does a physical invariance of Maxwell equations to Galilean transforms exist?
– 503. What does the physical invariance of Maxwell equations to Galilean transforms prove?
– 504. Does a physical invariance of Maxwell equations to Lorentz transforms exist?
– 505. Can the invariance of Maxwell equations to Lorentz transforms reflect reality if the unity axiom refers Lorentz transforms to the theoretical viruses?
– 506. Why do Maxwell equations describe the results of some experiments satisfactorily?
– 507. In what field of electrodynamics can Maxwell equations be used?
– 508. What properties should the equations have, which substitute Maxwell equations in a description of a process of propagation of energy and information in space?
– 509. Does Planck constant manifest its influence when the biological structures are formed?
– 510. Why is the overwhelming majority of the snails and the sea shells twirled counterclockwise?
– 511. Are there any sign of Planck constant realization in a human body?
– 512. What role will the law of formation of the spectra of the atoms and ions play, from which a lack of orbital motion of the electron in the atom results?
– 513. Will new understanding of physical and chemical processes simplify a study of the microworld?
– 514. Can future physics of the microworld be separated from chemistry of the microworld?
– 515. How much time will a new generation of physics and chemists need in order to master the judicial functions of the unity axiom?
– 516. What harm was done to physics of the 20th century by a prevalence of the persons with the first mathematical education and the second physical education or physical self-education among the physicists-theoreticians?
– 517. Will the international community of physicists understand that it is necessary to increase quantity of physicists who have the first physical education and the second mathematical one, bit vice versa?
– 518. Will the corollaries of the unity axiom be recognized as the third fundamental generalization in exact sciences?
– 519. Is there any reason to suppose that a new theory of the microworld will become a theoretical base of nanotechnologies?
– 520. The second edition of the study guide Course of lectures in physchemistry of the microworld (540 pages) has already been edited. Can the existing scientific elite understand that it is necessary to introduce a course of lectures in physchemistry of the microworld in to the educational process?
– 521. Can the course of lectures in physchemistry of the microworld be included into the educational process without an imperative order?
– 522. Has the Russian government the experts who can estimate a necessity of a transit to the study of new information concerning the microworld?
– 523. What country will be the first to adopt a decision to include new scientific information concerning microworld into the educational process and what influence will be exerted on its development?
– 524. Why has it become possible to find a solution of urgent global problems of fundamental sciences on in the language of the Russian ideation?
– 525. What properties of the Russian language have made it possible to get the new scientific results of the fundamental sciences?
CONCLUSION
Those whod like to know the details of the answers can advert to the source: Kanarev Ph.M. The Foundations of Physchemistry of the Microworld. 8th edition, Krasnodar 2007, 750 pages. Run: 100 copies